ClassificationSet is a subpattern of the set pattern. ClassificationSet is used for dynamic classification of elements. ClassificationSet defines two additional attributes:
- subsets: is a set containing the subsets of this classificationSet.
- insertSubset: takes a classificationSet and inserts it as a subset of this classificationSet. The exception illegalSubset will be invoked if the subset inserted contains elements, that are not instances of a subpattern of the element type of this classificationSet.
- superSet: if this classificationSet is a subset of another classificationSet, superSet will reference that classificationSet.
- scanUnclassified: like scan except that it only scans those elements that are not member of any subsets of this classificationSet.
Let us illustrate by an abstract example, assuming that css1 contains the elements a, b and c, css2 contains the elements c, d and e, and finally cs contains the elements b and f:

Then after
cs will contain the original elements, and the css1 subset:
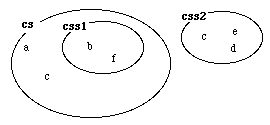
Note that the element b, originally located in both cs and css1, now is located exclusively in css1. In this situation, cs.scan(# ... #) will run through the elements a, b, c, d, e and f. and css1.scan(# ... #) will run through the elements b and f.
If we then execute
we will have the following situation:
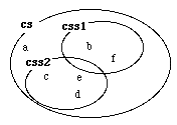
Note again, that c is exclusively in css2. If we now execute
g[]->css1.insert; f[]->css2.insert; b[]->cs.delete |
we will have the following situation:
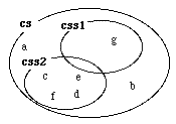
Finally,
css1.scanUnclassified(# ... #) |
will only scan the elements a and b, whereas
will scan all elements (i.e. a, b, c, d, e, f and g).
| Container Libraries - Reference Manual |
© 1992-2004 Mjølner Informatics |
[Modified: Thursday October 19th 2000 at 12:51]
|




